Date : 26 March 2024
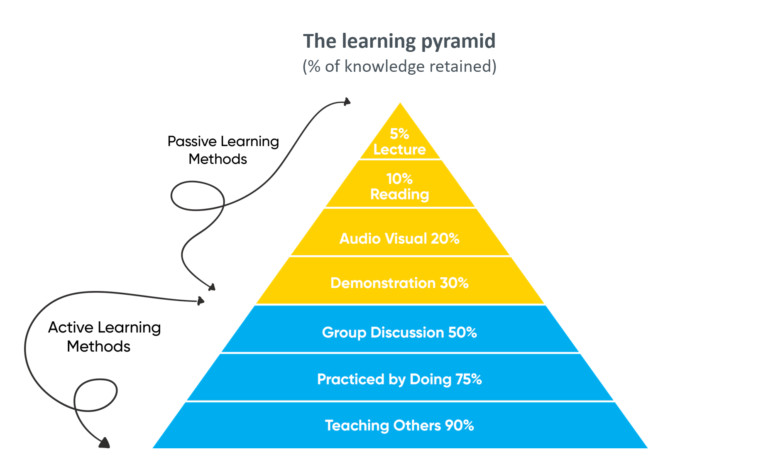
The
learning pyramid, also known as the "cone of
learning" or "cone of experience," is a visual
representation of different methods of learning
and their effectiveness in retaining information
over time. While the exact percentages associated
with each method can vary depending on the source
and context, the general concept remains
consistent. One of the methods often included in
the learning pyramid is teaching others, which is
considered one of the most effective ways to
solidify one's understanding of a topic. Here's a
detailed explanation of the learning pyramid
including teaching others:
Lecture: Lectures involve
passive listening to an instructor presenting
information. According to the learning pyramid,
retention rates from lectures are typically low,
ranging from around 5-10%. This method relies
heavily on auditory learning and does not offer
much interaction or engagement.
Reading: Reading involves
actively engaging with written material. Retention
rates from reading vary but are generally higher
than those from lectures, ranging from around
10-20%. Reading allows learners to digest
information at their own pace and revisit concepts
as needed.
Audio-Visual: Audio-visual
methods include watching videos, presentations, or
demonstrations. Retention rates from audio-visual
learning are higher than those from lectures or
reading, typically ranging from around 20-30%.
This method combines auditory and visual learning,
making it more engaging and memorable for many
learners.
Demonstration: Demonstrations
involve observing someone perform a task or
activity. Retention rates from demonstrations are
higher than those from passive methods like
lectures but lower than those from active methods
like teaching others. They typically range from
around 30-40%. Demonstrations provide visual and
sometimes hands-on learning experiences, allowing
learners to see concepts in action.
Discussion: Discussion involves
actively participating in conversations or group
activities related to the topic being learned.
Retention rates from discussion are higher than
those from passive methods but lower than those
from active methods like teaching. They typically
range from around 50-60%. Discussions encourage
critical thinking, collaboration, and the exchange
of ideas among learners.
Practice by Doing: Practice by
doing, also known as hands-on learning or
experiential learning, involves actively engaging
with the material through activities, exercises,
or simulations. Retention rates from hands-on
learning are higher than those from passive or
semi-active methods, typically ranging from around
75-90%. This method allows learners to apply
theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios,
reinforcing their understanding through practical
experience.
Teaching Others: Teaching
others involves explaining concepts or
demonstrating skills to someone else. Retention
rates from teaching others are among the highest
of all learning methods, often cited as around
90%. Teaching requires learners to organize their
thoughts, articulate concepts clearly, and
anticipate questions from the audience, leading to
a deeper understanding of the material.
In summary, the learning pyramid suggests that
actively engaging with the material, such as
through discussions, hands-on activities, and
teaching others, leads to higher retention rates
compared to passive learning methods like lectures
or reading. Teaching others, in particular, is
highlighted as an extremely effective way to
solidify one's understanding of a topic and retain
information in the long term.